Alcian Blue 8GX C.I. No: 74240
Properties
UV-VIS range: 611-620nm in water
Min. Dye Content: 50%
Molecular Formula: C56H68Cl4CuN16S4
Formula Weight:1298.88
Appearance: Dark blue-violet powder
Dye Class: Phthalocyanin
Biological Applications: differential stain for acidic polysaccharides, distinguishing sulfomucins, sialomucins and uronic acid mucins.
Commercial Applications: Dye print cellulosic substrates and as a gelling agent for lubricating oils.
Note: Currently (as of 12/13/00), there appears to be a shortage of Alcian Blue due to the lack of production. Efforts are currently being made by at least one manufacturer to produce BSC certified Alcian Blue 8GX. Also, substitute dyes are being testing in procedures calling for Alcian Blue 8GX. One substitute dye for these procedures that proves to work well is the Alcian Blue Pyridine Variant, which was used to prepare the following stains and the stained sections shown below.
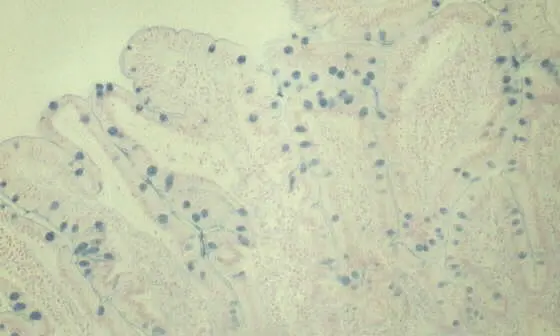
Mowry's Alcian Blue Method (pH 2.5)4
Preparation of Solutions
3% Acetic Acid Solution
Glacial Acetic Acid 3.0ml
Distilled Water 97.0ml
1% Alcian Blue Solution
Alcian Blue 8GX 1.0gm
3% acetic acid 100.0ml
Nuclear Fast Red Solution
Nuclear Fast Red 0.1gm
5% aluminum sulfate in water 100.0ml
add a few grains of thymol
- Deparaffinize and hydrate to distilled water.
- Place in 3% acetic acid for 3 minutes.
- Place in Alcian Blue solution for 30 minutes.
- Wash in running tap water for 2 minutes.
- Rinse in distilled water.
- Counterstain in nuclear fast red for 5 minutes.
- Rinse in 3 changes of distilled water.
- Dehydrate in graded alcohols.
- Clear in xylene.
- Mount sections with a synthetic resin.
Results: Acid sulfated mucosubstances - blue, Nuclei - red.
Scott's Alcian Blue Method (pH5.7)5,6,7
Preparation of Solutions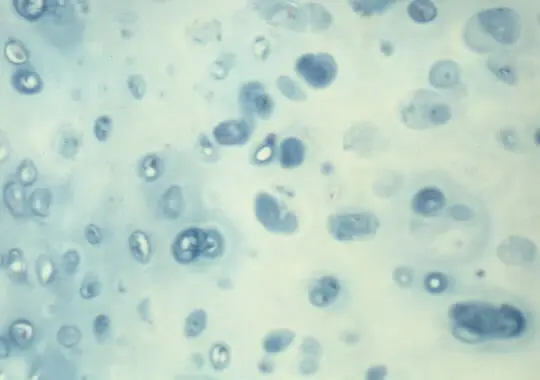
1.0M Sodium Acetate
Sodium Acetate 13.61gm
Distilled Water 100.0ml
add a few grains of thymol
1.0M Acetic Acid
Glacial Acetic Acid 5.7ml
Distilled Water 94.3ml
1.0M pH5.7 Sodium Acetate-Acetic Acid Buffer
1.0M sodium acetate 91.6ml
1.0M acetic acid 8.4ml
add a grain of thymol
4M Magnesium Chloride
Magnesium Chloride 8.13gm
Distilled Water 10.0ml
0.05M pH5.7 0.025% Alcian Blue with 0.3M Magnesium Chloride
1.0 pH 5.7 buffer solution 24.0ml
4M Magnesium Chloride 3.6ml
Alcian Blue 8GX 24mg
Distilled Water 42ml
Buffer Rinse Solution
1.0M pH5.7 buffer 72.0ml
4M Magnesium Chloride 108.0ml
Distilled Water 1260.0ml
Note: the final dye solution should be clear.
Staining Procedure:
- Deparaffinize through xylene.
- Hydrate sections through graded alcohols.
- Stain overnight in pH5.7 Alcian Blue solution.
- Rinse in three changes of distilled water
- Counterstain sections in Nuclear Fast Red solution (see Mowry's Method Above).
- Rinse in three changes of distilled water.
- Dehydrate sections in graded alcohols
- Clear in three changes of xylene.
- Mount sections with a synthetic resin.
Results: Polysulfates are stained turquoise blue. Mast cells, sulfated epithelial mucins, and cartilage matrix stains deep blue.
REFERENCES:
1.Lillie, R.D. 1977. H.J. Conn's Biological Stains, 9th edition. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore. pp. 452-455.
2.Sheenan, D.C., B.B. Hrapchak. Theory and practice of histotechnology, 2nd edition. Battelle Press, Columbus. pp. 172-173.
3.Green, F.J. 1990. The Sigma-Aldrich Handbook of Stains, Dyes and Indicators. Aldrich Chemical Comnpany, Milwaukee. pp.71-72.
4.Churukian, Charles J. 1989, Manual of the Special Stains Laboratory, 4th edition. University of Rochester, Rochester. pp. 55-56.
5.Scott, J.E., Dorling J. and Quintarelli, G. Differential staining of acid glycosaminoglycans by Alcian blue in salt solutions. Biochem.J. 1964. 90:4p.
6.Scott, J.E. and Dorling, J. (1965). Differential staining of acid glycosaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides) by Alcian blue in salt solutions. Histochemie. 5:221-233.
7.Mowry, R.W. and Scott, J.E. Observations on the basophilia of amyloids. Histochemie. 10:8-32, 1967.
8.Churukian, Charles J., Frank, M., and Horobin, R.W.. Alcian Blue Pyridine Variant - a Superior Alternative to Alcian Blue 8GX: Staining Performance and Stability. Biotechnic & Histochemistry. v75n3:147-150.May, 2000.
Stained sections shown above were provided to the BSC by Charles Churukian of the Special Stains Laboratory at the University of Rochester. Mowry's Alcian Blue PAS on formalin fixed bowel. Scott's Alcian Blue pH 5.7, formalin fixed trachea.